
Bariatric specialist examination
Bariatric surgery is the surgical treatment of obesity. When traditional treatments, such as dieting or even drug therapy, do not help, surgery can be an effective solution.
Bariatric surgery is the surgical treatment of obesity. When traditional treatments, such as dieting or even drug therapy, do not help, surgery can be an effective solution by reducing the volume of the stomach or improving the absorption of nutrients.
Morbid obesity can be associated with a complex set of diseases, which can be summarized together as metabolic syndrome. Obesity causes metabolic problems, the risk of cancer is also higher, it has a negative effect on the cardiovascular system and breathing, patients cannot breathe properly due to obesity, sleep apnea may also develop. The incidence of asthma is also increased, as is the incidence of high blood pressure and diabetes, which ultimately leads to more serious heart disease. If any surgery is needed, the risk is much higher in anesthesia and in the procedure itself. And surgeries are often unavoidable, as excess weight damages joints and wears out cartilage. As a result, life expectancy is reduced.
The surgical treatment of obesity - bariatric surgery - is a rapidly expanding surgical branch. The reason for this is that obesity is an increasingly serious problem in the developed world, and that surgery can be a solution if traditional treatments, such as dieting and drug therapy, fail.
Bariatric surgery options
There are two main groups of bariatric surgeries: restrictive (reducing stomach capacity) and malabsorptive (in addition to the former, the absorption of nutrients is also changed). Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) belongs to the family of restrictive surgeries. Among the malabsorptive surgical types, laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (LRGB) was the “gold standard” procedure in bariatric surgery for many years, until LSG gained ground and more recently the simpler, technically easier to perform mini or omega-loop or single-bypass gastric bypass (laparoscopic one-anastomosis/single-anastomosis/omega-loop gastric bypass (OAGB/SAGB).
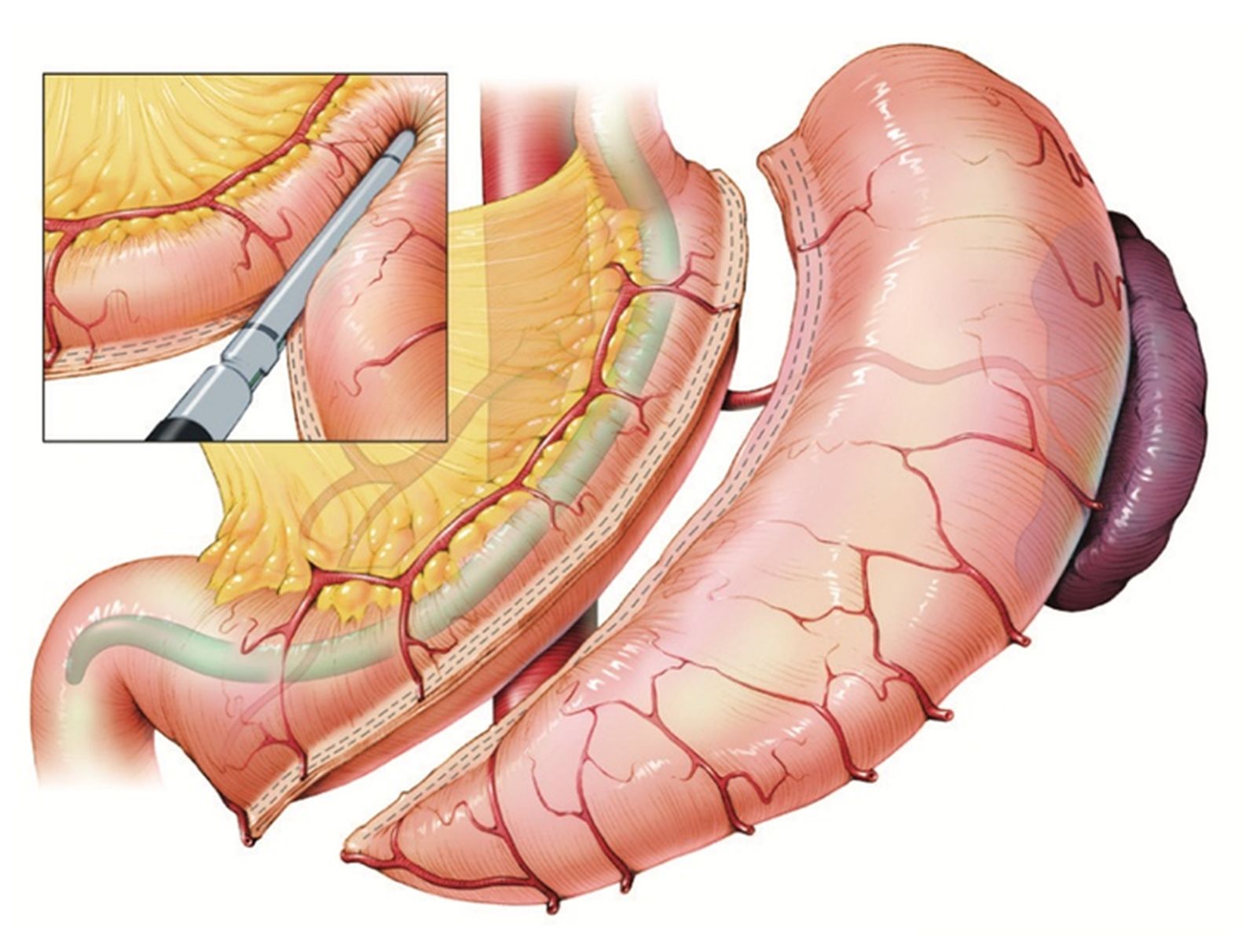
These surgeries are performed laparoscopically (keyhole surgery), with instruments introduced into the abdominal cavity through small incisions.
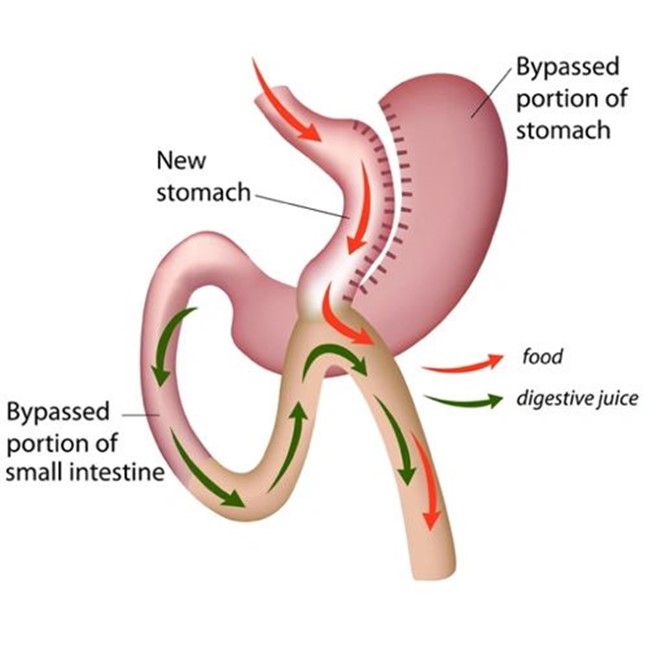
Sleeveless gastric bypass
This type of surgery is recommended for people with a body mass index (BMI) over 35. The primary goal of the procedure is not aesthetic: in addition to the weight loss after surgery, many diseases related to excess weight also improve, and in many cases are cured. For example, type 2 type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, sleep apnea, infertility or joint wear and tear. Losing weight significantly reduces the likelihood of developing many types of cancer, and self-esteem and confidence also improve. Overall, patients who have undergone surgery live longer and healthier lives.
The essence of sleeve gastrectomy is that a significant part of the stomach is removed. Only a narrow, approx. 3 cm in diameter, "tube" with a capacity of approx. 150-200 ml remains from the stomach, so the patient can only consume a smaller amount of food. The food consumed causes a feeling of fullness sooner and for a longer period of time. The patient also feels less hungry, because the cells that produce the "hunger hormone" (ghrelin) are also removed with the removed stomach section.
After the procedure
In the 18-24 months following the procedure, patients usually lose 70-80% of their excess weight, but success requires lifestyle changes in addition to the surgery. Continuous adherence to the diet and the introduction of exercise are also essential parts of the plan.
Thanks to the modern laparoscopic surgical procedure, the hospital stay is short: patients can usually go home the morning of the second day after the surgery, and if they do not do physical work, they can return to work after 5 days.
Tummy tuck is the most commonly used surgical solution for the treatment of excess weight in the USA, Canada and Asia, and the number of procedures performed is also rapidly increasing in the rest of the world. The reason for its popularity is that its effectiveness is similar to gastric bypass, and there are fewer complications, such as suture failure or internal hernia, and the risk of developing hair loss due to malabsorption, osteoporosis, iron deficiency, anemia, and vitamin deficiency later on.
Before surgery
The following examination is required before surgery to determine the risks of the surgery and its feasibility: bariatric surgery specialist consultation, gastroscopy examination (endoscopic examination of the upper digestive tract), dietetic consultation, psychological consultation, an anesthetist examination, chest X-ray, laboratory tests and other examinations may also be performed if necessary. We are happy to help organize these.
 Log in with GoodID
Log in with GoodID